Configuring Oblivious DNS Over HTTP (ODoH) protocol
Updated Date: 01/27/2026
This section enable you to understand the basic concept of ODoH functionality.
The Oblivious DNS over HTTPS (ODoH) protocol improves the privacy of DNS operations. This is achieved through a layer of public key encryption (HPKE) and a network proxy between clients and a DNS server. When ODoH is enabled, it does not allow any one server entity to be aware of both the client’s IP address and the content of the DNS queries and answers.
The following are components of ODoH:
- Client: Sends the encrypted query to proxy.
- Proxy: Receives the query from the client and sends the proxy query to the server. Returns the encrypted response from the server to the client.
- Server (Target): Receives and decrypts the query from the proxy and returns the encrypted response to the proxy. The ODoH target can be a virtual server with an HPKE key profile and GTM listener.
The following is an example scenario:
- When a client makes a DNS query using ODoH, its request is first encrypted using a public-key encryption scheme (HPKE).
- The request is then routed through a proxy that forwards the encrypted query to the DNS server.
- The DNS server can decrypt the query and sends the encrypted response back to the proxy, which returns it to the client.
This ensures that the DNS server never sees the client’s IP address, and the proxy never sees the unencrypted query, providing strong DNS privacy.
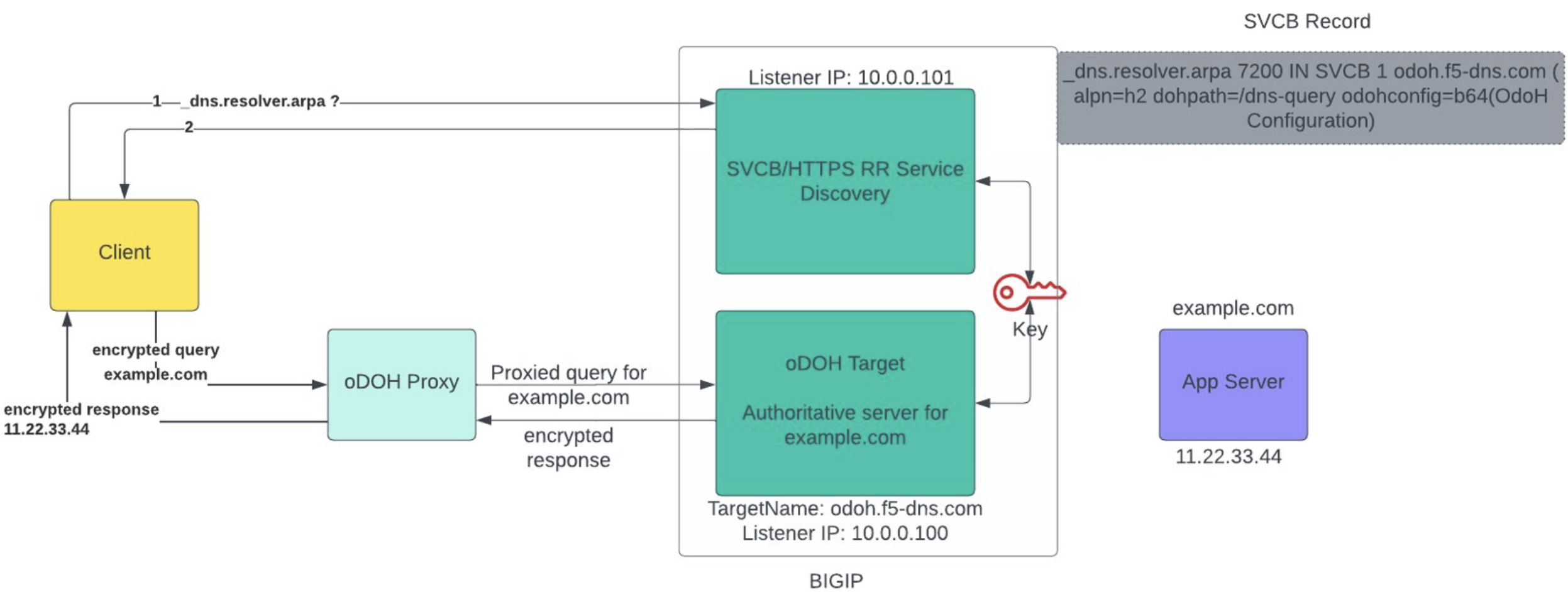
The ODoH uses Hybrid Public Key Encryption (HPKE), a versatile and modern cryptographic scheme that provides authenticated public key encryption for DNS queries. The clients encrypt their DNS queries with the DNS resolver’s public key, ensuring that only the resolver can decrypt the queries. Even if the proxy intercepts the communication, it cannot read the DNS query because it does not have the private key.
The HPKE key management is an automated process that handles the lifecycle of encryption keys, including creation, rollover, and expiration. A designated BIG-IP GTM/DNS is responsible for managing these keys.
BIG-IP DNS already supports popular DNS Resource Records (RR) like A, AAAA, and CNAME.
To support modern DNS-based service discovery and load balancing using the ODoH protocol, BIG-IP now includes support for Service Binding (SVCB) (Type64) and HTTPS RR (Type65). These records integrate with the Wide IP and Pool objects (GTM pools and pool members) to process and respond to DNS queries effectively.
Note:
- Configuring SVCB and HTTPS RR in BIG-IP is currently limited to supporting the ODoH protocol.
- The statistics for SVCB and HTTPS RR are included in the GTM statistics.
Perform the following tasks to implement the ODoH protocol:
- Generating HPKE key
- Create an HPKE profile
- Create an HPKE key
- Defining an ODoH target
- Create a data center
- Create a GTM server with the automatic virtual server discovery
- Create a DNS profile for the ODoH target
- Create a DoH Server listener using the DNS profile for ODoH target
- Create a GTM pool with DoH target as member
- Configuring a Wide IP
- Create a GTM wide IP with the GTM pool as member
- Create a GTM pool of type SVCB
- Create a Wide IP of type SVCB
- Configuring a DNS listener for SVCB/HTTPS records
- Create a DNS profile
- Create a listener with the DNS profile
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, click DNS > Delivery > Profiles > Other > HPKE Profile. The HPKE Profileuicontrol> screen opens.
-
Select Create
-
On the General Properties section, specify this information:
**Name:**The name of the HPKE profile that can be linked to the HPKE Key. **Description:**The text that provides the additional detail of the HPKE profile. **KEM:**The Key encapsulation method used to encrypt message. **KDF:**The Key Derivation Function algorithm. **AEAD:**The Authentication encryption method associated with data.
-
Specify this information in the Key Settings section:
**Rollover Period:**The interval after which the system generates a new key.
Note: By default, the value of the first key generation is 0 (zero) to indicate no rollover. Make sure the rollover period is more than or equal to half of the Expiration Period value. It must also be less than the value given in the Expiration Period. The value of ID is incremented by 1 for each key generation.
**Expiration Period:**The interval after which the system deletes a key.
Note: By default, the value is 0 to indicate that the key does not expire. The value of the expiration period must be more than the value given in the Rollover Period. Also, the difference between the values of the rollover and expiration periods must be more than the value of the TTL. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recommends that a zone signing key expire in 30 days, and that a key signing key expire once a year.
-
Click Finished to complete the task.
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, click DNS > Delivery > Keys > HPKE Key List . The HPKE Key List screen opens.
-
Click Create.
-
On theGeneral Properties section, specify this information:
**Name:**The name of the HPKE Key. **Description:**The text that provides the additional details of the HPKE Key. **HPKE Key Profile:**The HPKE profile that must be associated with the HPKE key.
-
Click Finished.
You can select the Generations tab to check the generated HPKE key.
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, click DNS > GSLB > Data Centres > Data Center List. The Data Center List screen opens.
-
Click Create.
-
In the General Properties section, specify this information:
**Name:**The name of the data center. **Description:**The additional information about the data centre. **Location:**The physical location of data center.The name of the HPKE Key. **Contact:**The name of the administrator or the name of the department that manages the data center. **Prober Preference:**The type of prober pools to use to monitor servers defined within the data center. The default value is Inside Data Center. Possible options:
Option Description Inside Data Center A server selects the probers from inside the data center where the server resides. Outside Data Center A server selects the probers from outside the data center where the server resides. Specific Prober Pool Select one of the Prober pools from the drop-down list. When assigning the Prober pool at the server level. Note: Prober pools are not used by the bigip monitor. **Prober Fallback:**The type of prober to use to monitor servers defined within the data center when the preferred type is not available. The default value is Any Available. Possible options:
Option Description Any Available For selecting any available prober. Inside Data Center A server selects probers from inside the data center where the server resides. Outside Data Center A server selects probers from outside the data center where the server resides. None No fallback probers are selected. Prober fallback is disabled. Specific Prober Pool Select one of the probers from the list When you want to assign a prober pool at the server level. **Availability:**Indicates the current status of the data center. The name of the HPKE Key. **State:**Indicates if the data center and its resources are available for load balancing. The value must be set to Enabled.
-
In the Devices section, specify the required fields.
-
In the Configurationsection, specify the required fields
-
In the Resourcessection, specify the required details.
-
Click Finished.
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, click DNS > GLSB > Servers > Server List. The Server List screen opens.
-
Click Create.
-
In the **General Properties:**section, specify this information:
**Name:**The name of the server host for DoH.The name of the data center. **Product:**The server type <Big-IP System>. The server type determines the metrics that the system can collect from the server. **Data Center:**The data center of the server. **Prober Preference:**The type of prober pools to use to monitor servers defined within the data center. The default value is Inside Data Center. Possible options:
Option Description Inside Data Center A server selects the probers from inside the data center where the server resides. Outside Data Center A server selects the probers from outside the data center where the server resides. Specific Prober Pool Select one of the Prober pools from the drop-down list. When assigning the Prober pool at the server level. Note: Prober pools are not used by the bigip monitor. **Prober Fallback:**The type of prober to use to monitor servers defined within the data center when the preferred type is not available. The default value is Any Available. Possible options:
Option Description Any Available For selecting any available prober. Inside Data Center A server selects probers from inside the data center where the server resides. Outside Data Center A server selects probers from outside the data center where the server resides. None No fallback probers are selected. Prober fallback is disabled. Specific Prober Pool Select one of the probers from the list When you want to assign a prober pool at the server level. **State:**Indicates if the server and its resources are available for load balancing. The value must be set to Enabled.
-
In the Devices section, specify the required fields.
-
In the Configuration section, specify the required fields
-
In the Resources section, specify the required details.
-
Click Finished.
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, click DNS > Delivery > Profiles > DNS. The DNS screen opens.
-
Click Create.
-
In the General Propertiessection, specify this information:
**Name:**The name <custom-dns-profile-odoh> of the DNS profile. **Parent Profile:**The DNS profile inherits the settings of this profile. The default value is dns.
-
Select the Custom checkbox to enable the optional fields.
-
In the DNS Features section, select the Oblivious DoHcheckbox.
-
Click Finished.
The ODoH Target is currently associated with a clientssl-secure profile which has a self-signed certificate. So, create a profile associated with Certificate Authority (CA) signed certificate or disable the certificate verification on the client side.
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, click DNS > Delivery > Listeners > GTM Listeners. The GTM Listeners List screen opens.
-
Click Create.
-
In the General section, specify:
**Name:**The name of the listener. **Description:**The descriptive text to identify the listener. **State:**Indicates if the listener is enabled or disabled to handle traffic.
-
In the Listener section with Basic options, specify this information:
**Destination:**The IP address to which the system listens for connections. The traffic sent to this IP address is processed. **VLAN Traffic:**The VLAN used by the system to listen for connection. Possible options:
Option Description All VLANS Applies to all the VLANS within the network segment. This option also applies if the system resides on a network segment that does not use VLANs. Enabled on Applies to the selected VLANs. Disabled on Applies to all the VLANs except the selected VLANs. -
In the Service section, specify this information:
**Protocol:**The protocol the listener uses. The default value is UDP. Possible options:
-
UDP
-
TCP **Protocol Profile (client):**The protocol profile that defines how clients communicate with this listener. The default is based on the protocol selected from the Protocol list. Possible options:
-
a list of system-supplied
-
user-defined protocol profiles **Protocol Profile (server):**The protocol profile that defines how servers communicate with this listener. Possible options:
-
Use Client Profile
-
System support
-
user-defined protocol profiles **DNS Profile:**Defines how the listener handles DNS traffic. The default is dns profile. Possible options:list of system-supplied user-defined DNS profiles **SSL Profile (client):**The SSL profile for managing client-side SSL traffic. Possible options:
-
HTTP Profile
-
HTTP/2 Profile (Client) When the listener is created, it is also added to the created GTM server. This is a virtual server on the device that is specified in the GTM Server.
-
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, clickDNS > GSLB > Pools > Pool List. The Pool List screen opens.
-
Click Create.
-
In the General section, specify this information:
**Name:**The name of the pool. **Type:**The type of pool or Wide IP. **State:**Indicates if the pool and its resources are available for load balancing.
-
In the Configuration section, select the Verify Member Availability checkbox and specify the required details.
-
In the Members section, specify the Load Balancing Method and other related fields.
-
Click Finished.
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, clickDNS > GSLB > Wide IPs > Wide IP List. The Wide IP List screen opens.
-
Click Create.
-
In the General section, specify this information:
**Name:**The name of the Wide IP. **Type:**The type (A) of pool or wide IP. **State:**Indicates that the system can use the wide IP and the resources for load balancing.
-
If required, specify the details in iRules section.
-
If required, specify the details in Pools section.
-
Click Finished.
Make sure that the wide IP and the HPKE Key are available to create Pool and wide IP with SVCB and HTTPS RR types.
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, clickDNS > GSLB > Pools > Pool List. The Pool List screen opens.
-
Click Create.
-
In the General section, specify this information:
**Name:**The name of the pool. **Type:**The type (SVCB) of the pool. **State:**Indicates that the system can use the pool and the resources for load balancing.
-
In the Configuration section, specify the required fields.
-
In the Members section, specify the required fields.
-
Click Finished.
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, clickDNS > GSLB > Wide IPs > Wide IP List. The Wide IP List screen opens.
-
Click Create.
-
In the General section, specify this information:
**Name:**The name of the Wide IP. **Type:**The type (SVCB) of pool or wide IP. **State:**Indicates that the system can use the wide IP and the resources for load balancing.
-
In the iRules section, specify the required fields
-
In the Pools section, specify the required fields.
-
Click Finished.
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, clickDNS > Delivery > Profiles > DNS. The DNS screen opens.
-
Click Create.
-
In the General section, specify this information:
**Name:**The name <custom-dns-profile> of the DNS profile. **Parent Profile:**The DNS profile inherits the settings of this profile.
-
Click Finished.
Do not enable the Custom checkbox.
-
Log in to the Configuration utility.
-
On the Main tab, clickDNS > Delivery > Listeners > GTM Listeners. The GTM Listeners screen opens.
-
Click Create.
-
In the General section, specify this information:
**Name:**The name <dohTargetNameResolver> of the listener. **Description:**The descriptive text to identify the listener. **State:**Indicates if the listener is enabled or disabled to handle traffic.
-
In the Listener section with Basic options, specify:
**Destination:**The IP address to which the system listens for connections. The traffic sent to this IP address is processed. For example: Host Address is 10.0.0.101 **VLAN Traffic:**The VLAN used by the system to listen for connection. Possible options:OptionDescriptionAll VLANSApplies to all the VLANS within the network segment. This option also applies if the system resides on a network segment that does not use VLANs.Enabled onApplies to the selected VLANs.Disabled onApplies to all the VLANs except the selected VLANs.
-
In the Service section with Basic options, specify this information:
**Protocol:**The protocol the listener uses. The default value is UDP. Possible options:UDPTCP **Protocol Profile (client):**The protocol profile that defines how clients communicate with this listener. The default is based on the protocol selected from the Protocol list. Possible options: a list of system-supplieduser-defined protocol profiles **Protocol Profile (server):**The protocol profile that defines how servers communicate with this listener. Possible options:Use Client ProfileSystem supportuser-defined protocol profiles **DNS Profile:**The DNS profile <custom-dns-profile> that defines how the listener handles DNS traffic. **SSL Profile (client):**The SSL profile for managing client-side SSL traffic. Possible options:HTTP ProfileHTTP/2 Profile (Client)
When the listener is created, it is also added to the created GTM server. This is a virtual server on the device that is specified in the GTM Server.
You can create multiple HPKE profiles using the TMSH commands.
Ensure that DNS is provisioned on the device, and the access is provided to the user for executing the TMSH commands. Following are the TMSH commands to configure ODoH.
-
Create a data center.
`tmsh create gtm datacenter testDC` -
Create a GTM Server. It can have the automatic virtual server discovery set as enabled to discover the listener which will act as the ODoH Target.It is needed to create HPKE keys later in this procedure.
`tmsh create gtm server odohServerHost { datacenter testDC devices add { ``10.0``.``0.3` `{ addresses add { ``10.0``.``0.3` `} } } virtual-server-discovery enabled }` -
Create an HPKE profile.
tmsh create ltm dns hpke profile hpke-profile -
Create an HPKE Key using the HPKE profile.
tmsh create ltm dns hpke key hpke-key profile hpke-profileVerify the key generation.
tmsh list ltm dns hpke keyFollowing is an example output:
ltm dns hpke key hpke-key { generation { 1 { creator bigip1.localdomain public-text X43zoccrC6LMDgkZBR8i9JDht3UrVhYn53P7FMdd+Ug= } } profile hpke-profile } -
Create a DNS profile for ODoH target.
`tmsh ltm profile dns odoh-dns-profile enable-odoh yes` -
Create a DoH Server listener with the DNS profile for ODoH target
-
When configured as the GTM listener:
tmsh `create gtm listener odohTarget address ``10.0``.``0.100` `port https ip-protocol tcp profiles add { odoh-dns-profile { } tcp { context clientside } udp_gtm_dns { context serverside } http { } http2 { } clientssl-secure { } }` -
When configured as the GTM DoH Server listener:
tmsh `create gtm listener-doh-server odohTarget address ``10.0``.``0.100` `port https profiles add { doh-server { } odoh-dns-profile { } tcp { context clientside } udp_gtm_dns { context serverside } http { } http2 { } clientssl-secure { } }`
-
-
Create a GTM Pool with DoH Target as a member.
tmsh create gtm pool a odohTargetPool members add { odohServerHost:/Common/odohTarget } -
Create a gtm wideip with the above pool as its member.
`tmsh create gtm wideip a odoh.f5-dns.com pools add { odohTargetPool }` -
Create a GTM Pool of type SVCB.
tmsh create gtm pool svcb odohTargetSVCBPool members add { odoh.f5-dns.com { hpke-key hpke-key } } -
Create a WideIP of type SVCB.
tmsh create gtm wideip svcb _dns.resolver.arpa pools add { odohTargetSVCBPool } -
Create a DNS profile.
tmsh create ltm profile dns custom-dns-profile -
Create a listener with the above profile.
`tmsh create gtm listener dohTargetNameResolver { address ``10.0``.``0.101` `profiles add { custom-dns-profile { } udp_gtm_dns { } } }`
The following are the log messages related to ODoH:
| S. No | Description |
|---|---|
| 011a0400 | There was an error trying to send a HPKE Key Generation %s msg to MCP. |
| 011a0401 | Setting date of new generation %s to NOW. |
| 011a0403 | Encountered error %s while trying to set a HPKE Key Generation event timer. |
| 011a0404 | Processing %s Event for HPKE Key %s, ID %llu. |
| 011a0405 | Unable to determine primary GTM, must skip processing HPKE Key Generation events. |
| 011a0406 | Failed to create new HPKE Key Generation %s:%llu due to %s. |
| 011a0408 | Postponing expiration of HPKE Key Generation %s:%llu as the next generation has not yet been created. |
| 011a0409 | Canceling expiration of the latest HPKE Key Generation %s:%llu, resetting events for the Key. |
| 011a040a | HPKE Key Generation %s:%llu action execution exceeded allowed processing time, canceling the action. |
| 011a040b | Action of HPKE Key Generation %s:%llu failed or canceled, rerunning the action. |
| 011a040c | Action of HPKE Key Generation %s:%llu failed or canceled, retry count exceeded. |
| 011a040d | Failed to join worker-thread of HPKE Key Generation. |
| 011a040e | Failed to re-encrypt HPKE Key Generation %s:%llu. |
| 011a040f | HPKE Key Generation %s:%llu created: %s and %s |
| 011a0410 | HPKE Key Generation %s:%llu : expired or removed from configuration. |
| 011a0411 | HPKE Key Generation %s:%llu expired. |
| 011ae119 | Master Key decryption failed: %s. |
| 011ae118 | Master Key encryption failed: %s. |
The following are the HTML error messages:
| HTML Message | HTTP Status Code |
|---|---|
| “No Error” | 200 OK |
| “ODoH requires header Accept:application/oblivious-dns-message” | 406 Not Acceptable |
| “ODoH Post requires header Content-type:application/oblivious-dns-message” | 415 Unsupported Media Type |
| “ODoH only supports POST method” | 400 Bad Request |
| “ODoH URL and method incompatible” | 400 Bad Request |
| “Invalid DNS Packet" | 400 Bad Request |
| “Key Mismatch” | 401 Authorized |
