Applies To:
Show Versions
BIG-IP AFM
- 11.4.1, 11.4.0
Overview: Configuring remote high-speed Network Firewall event logging
You can configure the BIG-IP® system to log information about the BIG-IP system Network Firewall events and send the log messages to remote high-speed log servers.
When configuring remote high-speed logging of Network Firewall events, it is helpful to understand the objects you need to create and why, as described here:
| Object to create in implementation | Reason |
|---|---|
| Pool of remote log servers | Create a pool of remote log servers to which the BIG-IP system can send log messages. |
| Destination (unformatted) | Create a log destination of Remote High-Speed Log type that specifies a pool of remote log servers. |
| Destination (formatted) | If your remote log servers are the ArcSight, Splunk, or Remote Syslog type, create an additional log destination to format the logs in the required format and forward the logs to a remote high-speed log destination. |
| Publisher | Create a log publisher to send logs to a set of specified log destinations. |
| Logging profile | Create a custom Logging profile to enable logging of user-specified data at a user-specified level, and associate a log publisher with the profile. |
| LTM® virtual server | Associate a custom Logging profile with a virtual server to define how the BIG-IP system logs security events on the traffic that the virtual server processes. |
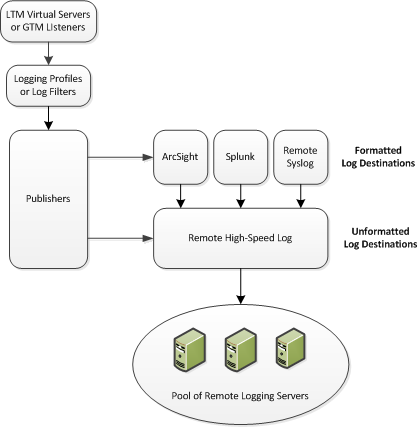 Association of remote high-speed logging configuration objects
Association of remote high-speed logging configuration objects
Task summary
Perform these tasks to configure remote high-speed network firewall logging on the BIG-IP® system.Creating a pool of remote logging servers
Creating a remote high-speed log destination
Create a log destination of the Remote High-Speed Log type to specify that log messages are sent to a pool of remote log servers.
Creating a formatted remote high-speed log destination
Create a formatted logging destination to specify that log messages are sent to a pool of remote log servers, such as Remote Syslog, Splunk, or ArcSight servers.





