Manual Chapter :
Configuring ISP Load Balancing
Applies To:
Show Versions
Configuring ISP Load Balancing
Overview: ISP load balancing
You might find that as your network grows, or network traffic increases, you require an additional connection to the Internet. You can use this configuration to add an Internet connection to your existing network. The following illustration shows a network configured with two Internet connections.
Illustration of ISP load balancing
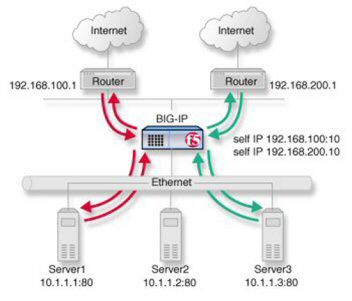
ISP load balancing
Creating a load balancing pool
Ensure that at least one virtual server exists in the configuration
before you start to create a load balancing pool.
Create a pool of systems with Access Policy Manager to which
the system can load balance global traffic.
Creating a virtual server for inbound content server traffic
You must create a virtual server to load balance inbound connections. The default pool that you assign as a resource in this procedure is the pool of internal servers.
The virtual server is configured to load balance inbound connections to the
servers.
Creating a virtual server for outbound traffic for routers
You must create a virtual server to load balance outbound connections. The default pool that you assign as a resource in this procedure is the pool of routers.
The virtual server is configured to load balance outbound connections to the
routers.
Creating self IP addresses an external VLAN
You must assign two self IP addresses to the external VLAN.
The self IP address is assigned to the external VLAN.
Enabling SNAT automap for internal and external VLANs
You can configure SNAT automapping on the BIG-IP system for internal and external
VLANs.
SNAT automapping on the BIG-IP system is configured for internal and external VLANs.





